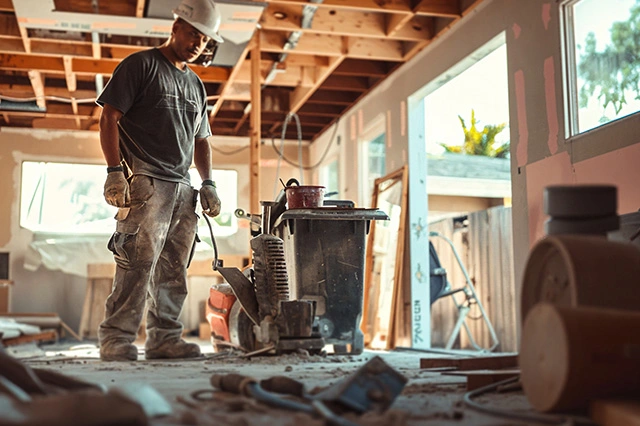
Tradesmen, often known as skilled manual workers or “tradies,” form the backbone of the UK’s construction, repair, and maintenance industries. Covering a broad spectrum of jobs—from electricians and plumbers to carpenters, bricklayers, painters, and decorators—these professionals contribute significantly to the economy and daily life in the UK. This article delves into the essential roles, challenges, and developments within the tradespeople industry in the UK.
1. The Scope of the Trades Industry in the UK
The trades industry in the UK is vast and varied, encompassing numerous specialties. Some of the main trades include:
- Electricians: They are responsible for installing, maintaining, and repairing electrical systems.
- Plumbers and Heating Engineers: Specialists who work on water supply, drainage systems, and heating systems in residential and commercial buildings.
- Carpenters and Joiners: Experts in working with wood, crafting furniture, frames, and structural elements.
- Bricklayers: Skilled in constructing and repairing walls, pathways, and other structures.
- Painters and Decorators: They bring the final touch to buildings, working on interior and exterior surfaces.
Each trade requires a unique set of skills, technical knowledge, and often formal qualifications and certifications, which ensure the safety and quality of their work.
2. Apprenticeships and Training for Tradespeople
The pathway to becoming a tradesman in the UK often begins with an apprenticeship. Apprenticeships combine practical, on-the-job training with classroom-based instruction, allowing trainees to earn while they learn.
Apprenticeships in trades can vary in length, generally taking between 2-4 years. Programs are available through colleges, vocational schools, and professional organizations. A growing number of tradespeople also pursue NVQs (National Vocational Qualifications) as well as certifications from industry bodies such as NICEIC for electricians and Gas Safe for plumbers.
The UK government has been investing in apprenticeships to address a shortage of skilled tradespeople and to encourage young people to pursue these careers. However, the success of apprenticeships depends on the availability of employers willing to provide mentorship and training for the next generation.
3. The Importance of Certification and Regulation
Certification is crucial in the trades industry, especially when working with electrical, gas, or plumbing systems. In the UK, specific certifications—like the Gas Safe Register for gas engineers—are mandatory. This regulation is essential to ensure the safety and legality of work performed. It’s a rigorous process that not only boosts the credibility of tradespeople but also ensures that they adhere to safety and performance standards.
4. Demand and Shortages in the Trades Industry
The UK has been facing a shortage of skilled tradespeople in recent years. Factors contributing to this shortage include an aging workforce, decreased interest among younger generations in trade careers, and Brexit, which affected the flow of skilled labour from Europe.
This shortage has led to increased demand, with many tradespeople reporting a steady flow of work and higher-than-average wages. For example, electricians, plumbers, and gas engineers are in particularly high demand, with some even facing waiting lists for clients. This demand has also highlighted the need for more government-backed training programs to bring new workers into the trades.
5. Advancements in Technology and Tools
Technology is reshaping how tradespeople work. The adoption of digital tools, such as mobile apps and online platforms, has improved efficiency in areas like job scheduling, quoting, invoicing, and client communication. Additionally, tradesmen are adopting advanced tools like thermal imaging cameras, drones for surveying, and laser measuring tools, which enhance accuracy and productivity.
Smart home technology is also creating new opportunities. As more UK households embrace smart appliances, security systems, and energy-efficient heating solutions, tradespeople need to stay updated with these new products, driving a trend of continuous learning within the industry.
6. Challenges Facing Tradespeople
Despite their essential role, tradespeople face several challenges:
- Late Payments: A persistent issue, especially for self-employed tradesmen and small businesses, is delayed payments from clients, which impacts cash flow and business sustainability.
- Job Security: While the demand for trades remains high, seasonal variations and economic downturns can impact job stability, particularly for self-employed or contract workers.
- Health and Safety: Tradespeople often work in physically demanding environments that carry risks of injury. The Health and Safety Executive (HSE) in the UK provides regulations, but maintaining health and safety standards is a constant concern.
- Public Perception: There has historically been a perception that trade jobs are “less skilled” compared to white-collar jobs, though this is changing with awareness of the complexity and necessity of these roles.
7. The Future of Trades in the UK
The future for tradespeople in the UK is promising, driven by ongoing demand, government initiatives, and a societal shift toward valuing skilled manual labor. The push toward eco-friendly solutions is creating new opportunities, especially in energy-efficient installations like solar panels, electric vehicle charging stations, and improved insulation methods. The UK’s focus on sustainable housing aligns well with the skills of tradesmen, positioning them as key players in achieving environmental goals.
8. Building a Successful Career as a Tradesman
For those interested in pursuing a trade, success often lies in building a reputation based on reliability, quality, and customer satisfaction. Networking and community engagement are also vital. Many tradespeople find that positive client relationships lead to word-of-mouth referrals, which remain a significant source of new business.
Investing in continued education, developing digital skills, and staying updated with industry trends can also help tradesmen remain competitive and capable of tackling modern challenges.